
Technical Business Analyst

A Technical Business Analyst is a professional who plays a critical role in bridging the gap between business objectives and technical solutions. They are responsible for understanding the business needs of an organization, analyzing those needs, and translating them into technical requirements that can be implemented by the development team.
Role And Responsibilities Of A Technical Business Analyst:
Requirement Gathering: Gather and document business requirements by working closely with stakeholders to understand their needs and objectives.
Analysis: Analyze existing business processes and identify opportunities for improvement through technology.
Translating Requirements: Translate business needs into clear and detailed technical requirements that can be understood by the development team.
Collaboration: Collaborate with various teams, including developers, quality assurance, and project managers, to ensure that technical solutions meet business requirements.
Testing Support: Assist in defining test cases and participate in testing to ensure that the developed solutions meet the specified requirements.
Documentation: Create and maintain documentation, such as use cases, user stories, and process flows, to communicate requirements and project details.
Risk Assessment: Identify and mitigate potential project risks and issues.
Testing Support: Assist in defining test cases and participate in testing to ensure that the developed solutions meet the specified requirements.
Change Management: Manage changes to project scope and requirements, ensuring that they are properly documented and communicated to stakeholders.
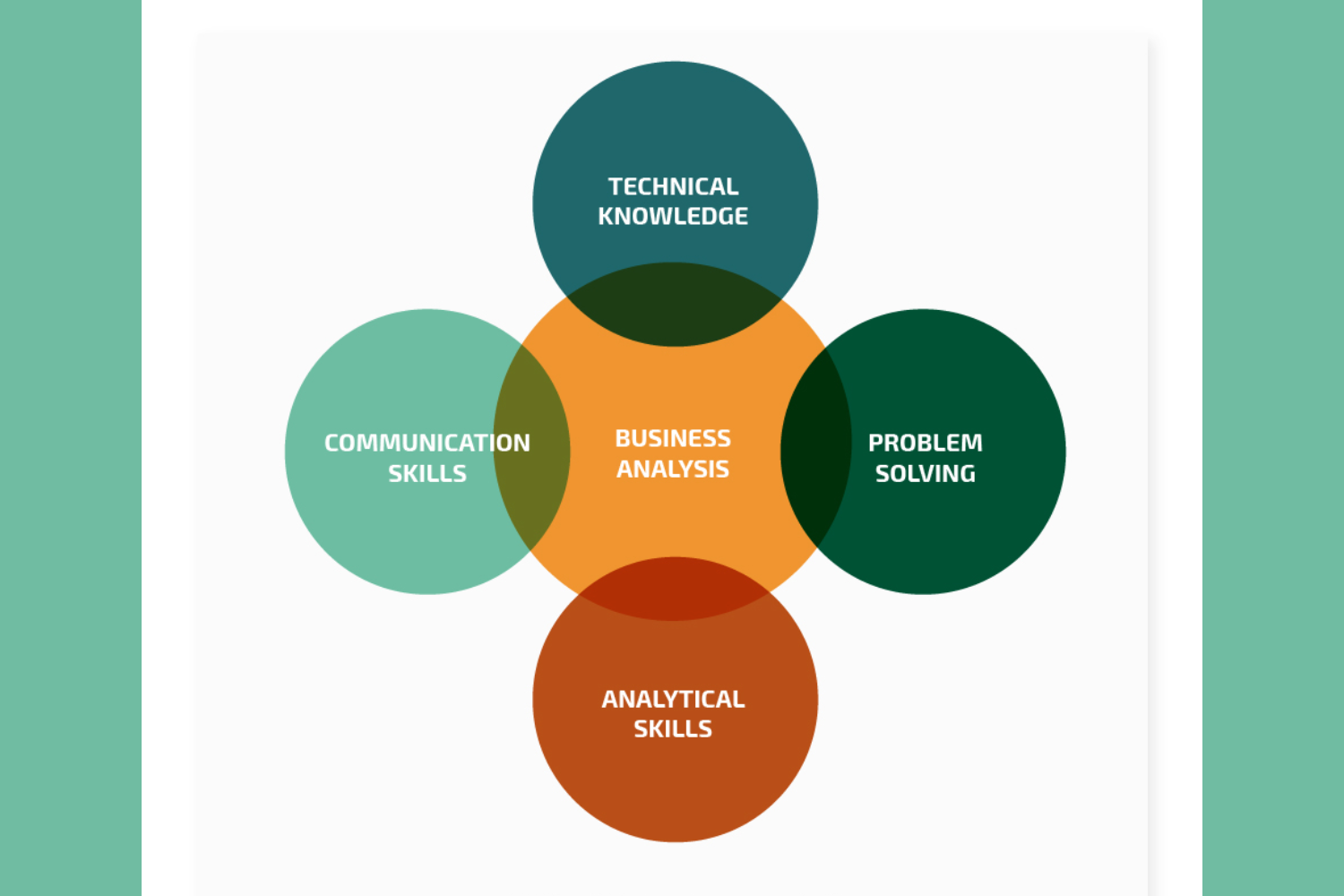
Communication: Effectively communicate technical details to non-technical stakeholders and convey business requirements to technical teams.
Technical Knowledge: Possess a strong understanding of the technical aspects of the solutions being developed.
Problem-Solving: Solve complex business problems using technical solutions and critical thinking.
Project Support: Provide support in project planning and monitoring, even though they are not typically project managers.
Qualities Of A Technical Business Analyst:
A Technical Business Analyst should possess a combination of technical knowledge and business acumen. They need strong analytical and problem-solving skills to identify opportunities for improvement, effective communication skills to bridge the gap between technical teams and business stakeholders, and the ability to document requirements and specifications clearly. Being a team player, adaptable, and customer-centric is essential, along with having strong time management and project management capabilities. Empathy, conflict resolution, and continuous learning are also important qualities, helping them navigate the complex interplay of technology and business to deliver successful projects that meet the organization’s goals and the needs of its customers.
How To Become A Technical Business Analyst:
Becoming a Technical Business Analyst typically involves a combination of education, skills development, and practical experience. Here are the steps to become a Technical Business Analyst:
1. Educational Background
2. Develop Core Skills.
a. Business Acumen
b. Technical Skills
c. Analytical Skills
3. Learn Business Analysis
4. Gain Technical Knowledge
5. Communication Skills
6. Hands-On Experience
7. Networking
8. Build a Portfolio
9. Apply for Positions
10. On-the-Job Learning
11. Adaptability
12. Continuing Education
Technical Business Analyst Career Paths:
A career as a Technical Business Analyst can lead to various paths and opportunities for growth.
1.Senior Technical Business Analyst
2. Business Systems Analyst
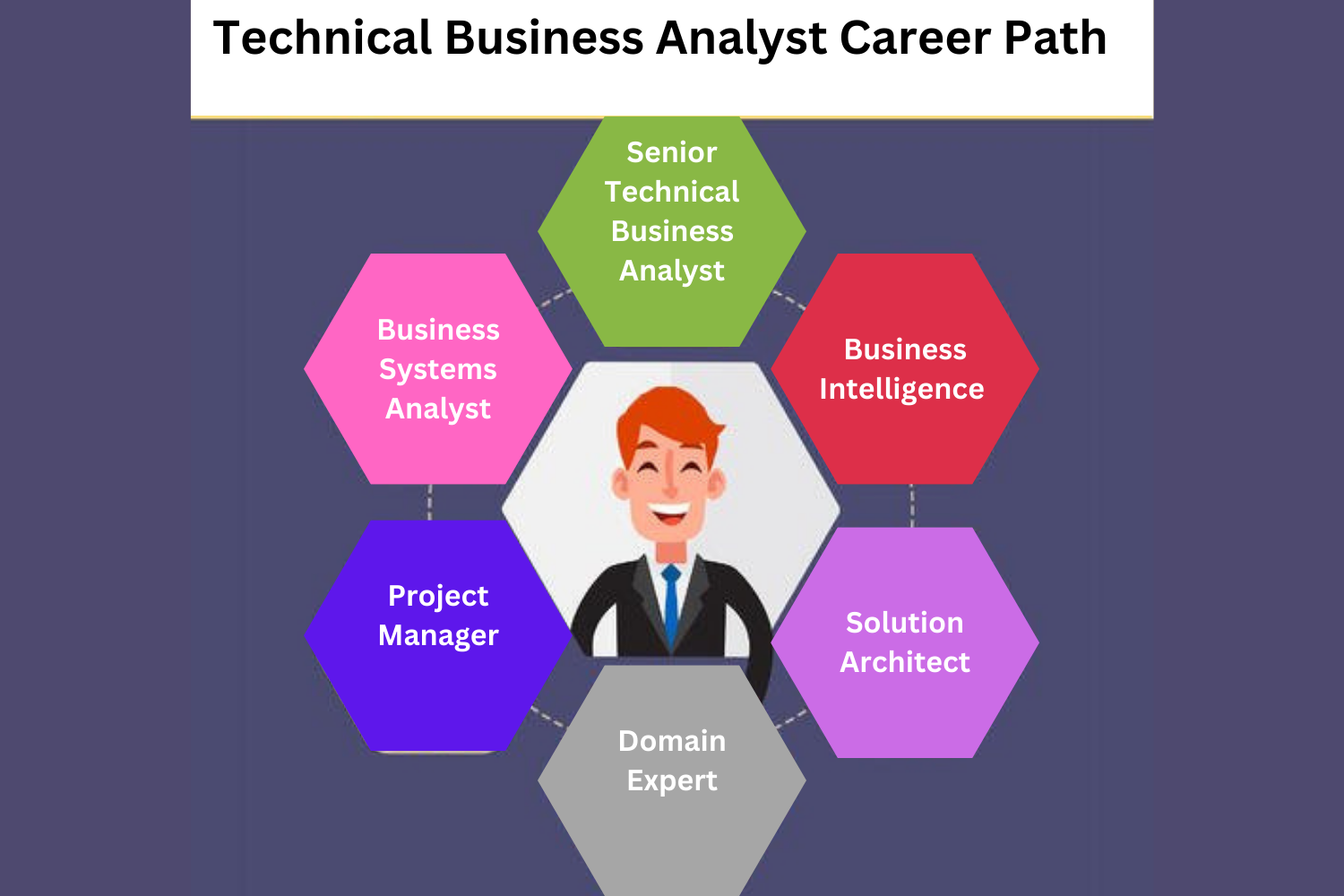
3. Product Owner or Product Manager
4. Project Manager
5. Data Analyst or Data Scientist
6. Business Intelligence Analyst
7. Solution Architect
8. Domain Expert
9. Entrepreneurship
Skills Of A Technical Business Analyst:
Here are some key technical skills that are valuable for business analysts:
1. Data Analysis
2. Business Intelligence (BI) Tools
3. Process Modeling and Analysis
4. Requirements Management
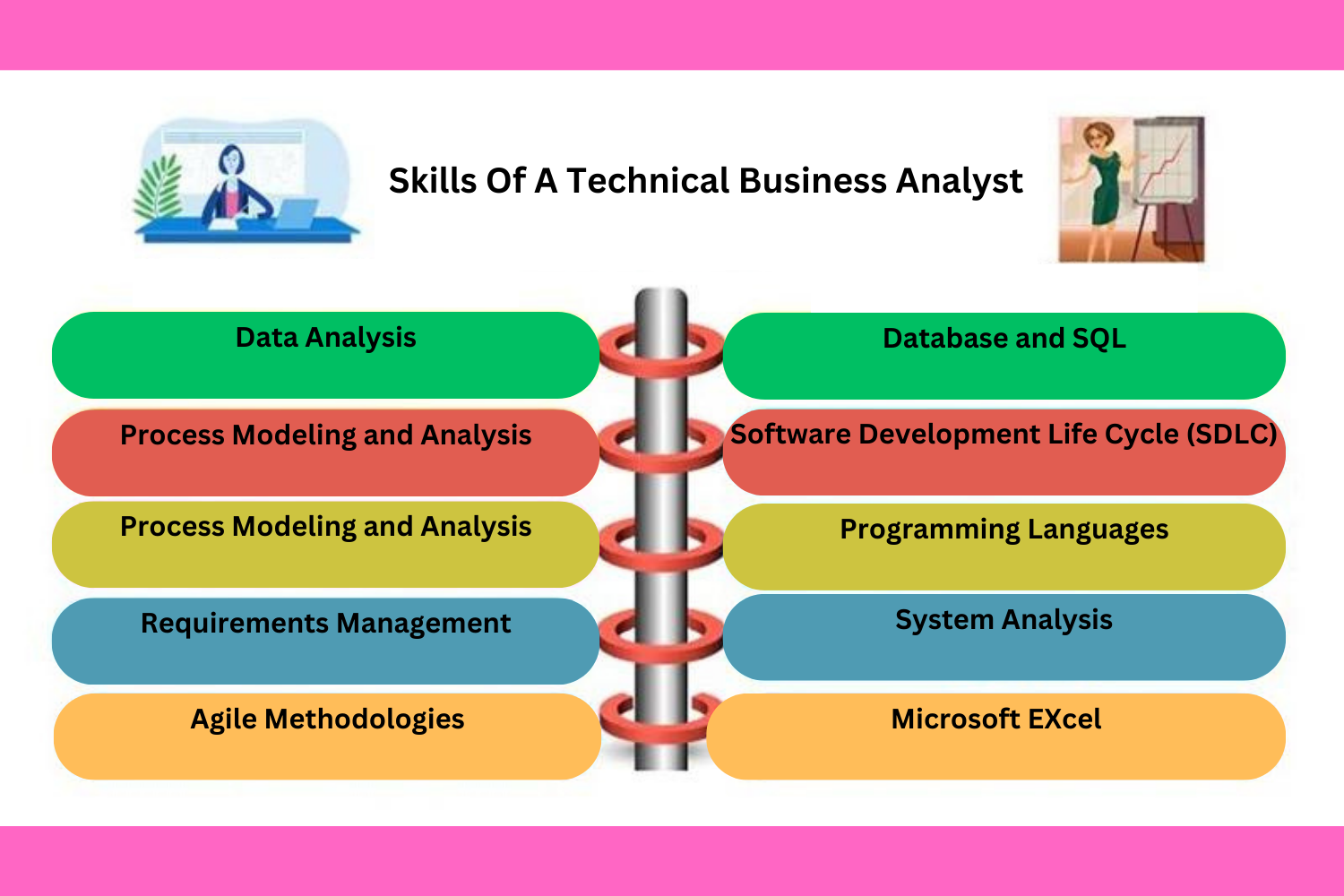
5. Agile Methodologies
6. System Analysis
7. Prototyping and Wireframing
8. Knowledge of ERP and CRM Systems
9. Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
10. Programming Languages
11. Creation of Reports and Dashboards
12. Database and SQL
13. Microsoft Excel
14. Documentation and Presentation
What Tools And Software Are Typically Used By Technical Business Analysts In Their Work?
Technical Business Analysts use a variety of tools and software to perform their roles effectively. These tools help them analyze data, document requirements, facilitate communication, and manage projects. Some common tools and software used by Technical Business Analysts include:
1. Microsoft Office Suite
2. Requirements Management Tools
3. Diagramming and Modeling Tools
4. Project Management Software
5. Data Analysis Tools
6. Version Control Systems
7. Database Management Tools
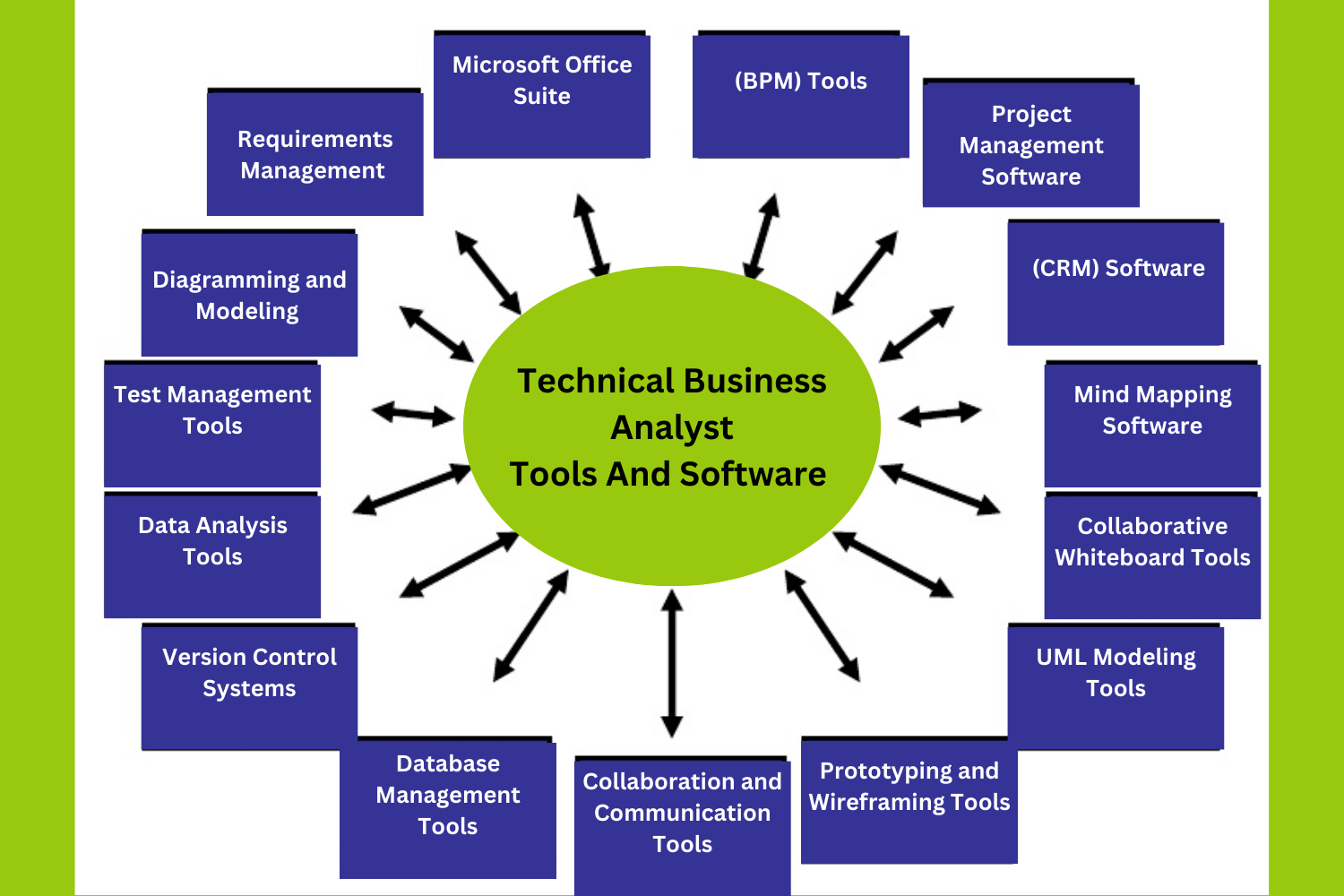
8. Collaboration and Communication Tools
9. Prototyping and Wireframing Tools
10. Mind Mapping Software
11. UML Modeling Tools
12. Screen Recording and Capture Tools
13. Documentation and Content Management
14. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Software
15. Business Process Management (BPM) Tools
16. Collaborative Whiteboard Tools
17. Test Management Tools
Salary Package of Technical Business Analyst:
Technical Business Analyst salary in India ranges between ₹ 13LPA-35LPA.
Course Highlights/ Details
1. Suited for students, fresher’s, professionals, and corporate employees
2. Live online classes
3. 4-month program
4. Certificate of completion
5. Decision Oriented Program of Analysis
6. Live Classes by highly experienced faculties
7. Hands-on experience with real-life case studies.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Technical Business Analyst’s role is pivotal in aligning technology with business goals. With a mix of technical expertise, business acumen, and strong communication, they bridge the gap between these domains, ensuring efficient project delivery and compliance with industry standards. Their adaptable nature and commitment to continuous learning make them invaluable assets in the ever-evolving tech landscape.

