
BaaS (Business as a Service)
While “Business as a Service” is not a widely recognized term, it could refer to the concept of delivering business functionalities or processes as a service. This could include various aspects of business operations being outsourced or provided through cloud-based services.

Possible Components:
Software as a Service (SaaS): Offering software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for users to install, maintain, and update software locally.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): Providing a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without dealing with the complexity of building and maintaining the underlying infrastructure.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Offering virtualized computing resources over the internet, including storage, computing power, and networking.
What is BaaS (Business-as-a-Service)?
A2P messaging pioneers BaaS gives mobile operators the ability to manage their whole A2P business without significant capital outlay or ownership risk.
The phrase “business-as-a-service” is taken from the common language that cloud solution developers use to identify various phases of development.

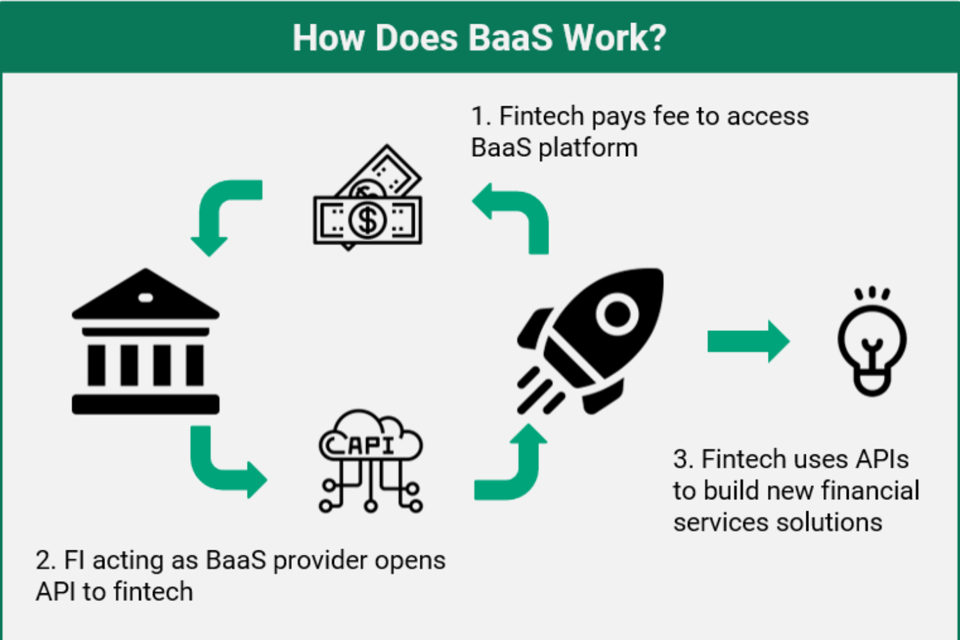
How does the Business-as-a-Service model work?
Typically, a specialized technology partner provides BaaS to mobile operators as a modular A2P messaging management and service delivery approach. A fully managed instance of a core communications platform is included, and it is updated and maintained in compliance with the most recent standards for operational services management, security and continuous service delivery, and infrastructure development.
Benefits of BaaS (Business-as-a-Service)?
1. Cost Reduction: BaaS models often allow businesses to reduce costs associated with infrastructure, software licensing, and maintenance.
2. Scalability: Businesses can scale their operations up or down based on demand without the need for significant upfront investments.
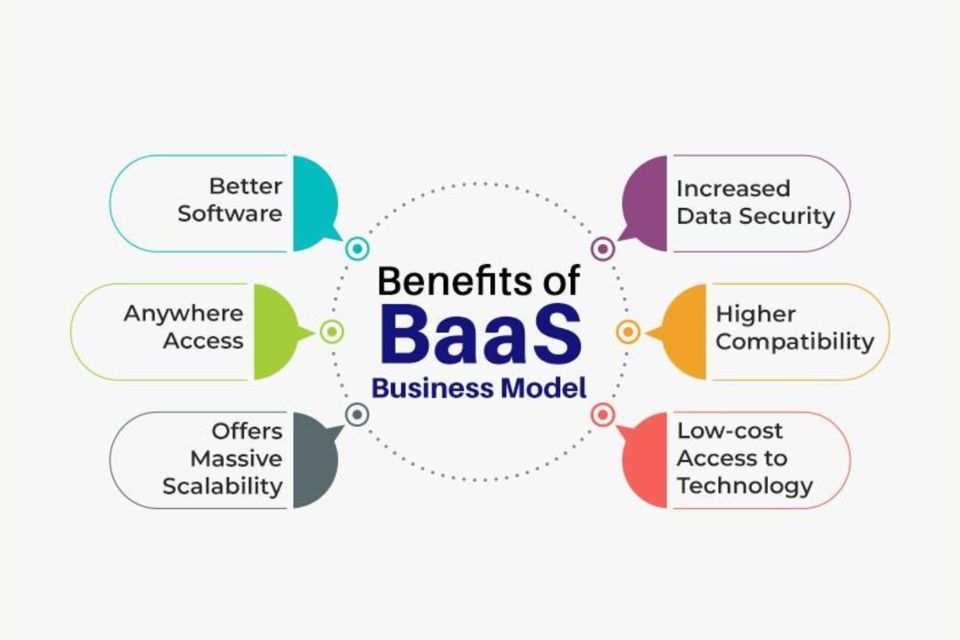
3. Focus on Core Competencies: Outsourcing non-core business functions allows companies to focus on their core competencies and strategic goals.
Types of BaaS (Business-as-a-Service)?
1. Finance as a Service (FaaS): Outsourcing financial tasks like accounting and payroll.
2. HR as a Service (HRaaS): Outsourcing human resources functions, including recruitment and employee management.
3. Marketing as a Service (MaaS): Outsourcing marketing activities such as digital marketing and social media management.
4. Software as a Service (SaaS): Accessing software applications over the internet on a subscription basis.
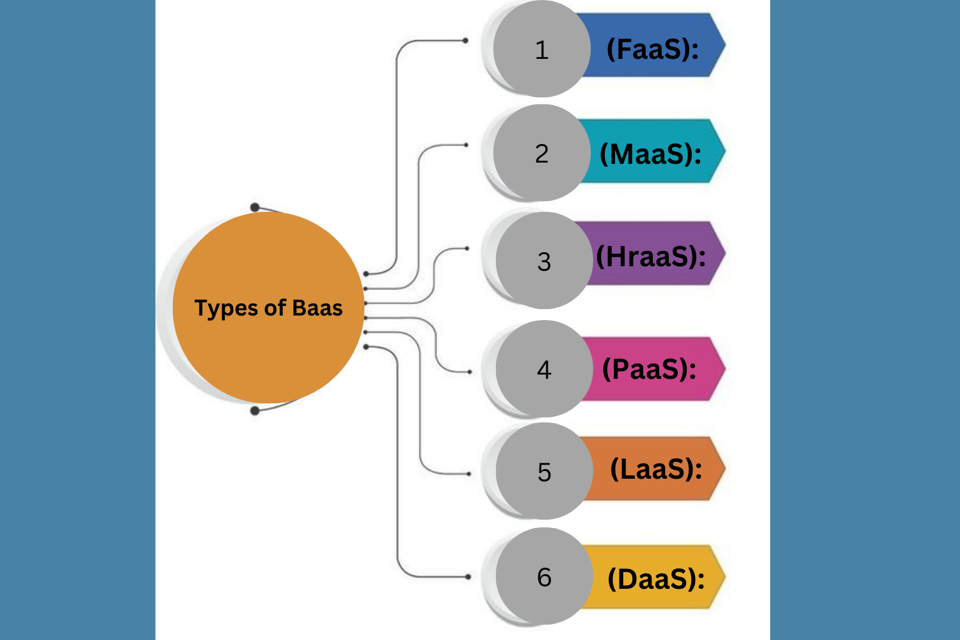
5. Platform as a Service (PaaS): Using a platform to develop and manage applications without dealing with infrastructure.
6. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Accessing virtualized computing resources over the internet.
7. Data as a Service (DaaS): Accessing datasets and data-related services for analytics.
8. Unified Communications as a Service (UCaaS): Using communication tools like video conferencing and messaging over the internet.
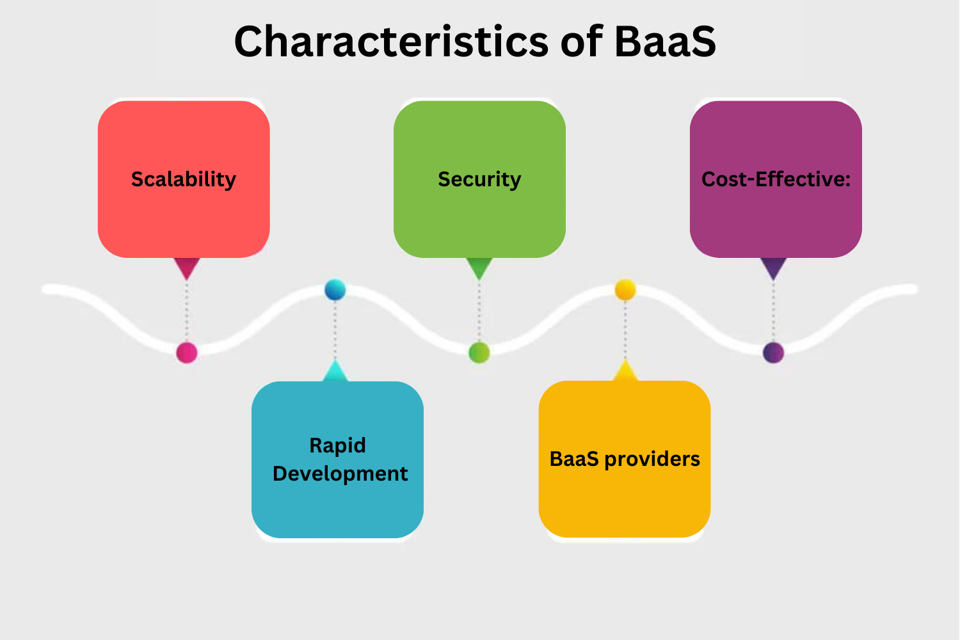
Characteristics of BaaS (Business-as-a-Service)?
1.Scalability: BaaS providers offer scalable solutions, enabling businesses to adjust their blockchain infrastructure according to their needs.
2.Security: BaaS leverages the inherent security features of blockchain, including cryptographic algorithms, to ensure data integrity and prevent tampering.
3.Cost-Effective: Instead of investing in the development and maintenance of a private blockchain, businesses can use BaaS on a pay-as-you-go basis, reducing initial costs.
4.Rapid Development: BaaS platforms typically come with pre-built templates and smart contract libraries, allowing developers to quickly create and deploy blockchain applications.
5.Examples of BaaS providers: Microsoft Azure, IBM Blockchain Platform, Amazon Managed Blockchain, and more.

Scope of BaaS (Business-as-a-Service)
The scope of Business as a Service (BaaS) extends to simplifying and optimizing various aspects of business operations. By leveraging BaaS, companies can outsource non-core functions, such as finance, human resources, and marketing, to specialized service providers. This outsourcing model enables businesses to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and gain access to expertise in specific areas without the need for extensive in-house infrastructure.
BaaS also provides the flexibility for organizations to scale their operations based on changing needs, fostering agility and adaptability in dynamic business environments. Ultimately, the overarching goal of BaaS is to empower businesses to concentrate on their core competencies, drive innovation, and stay competitive in an ever-evolving market.
Technologies of BaaS (Business-as-a-Service)?
Business as a Service (BaaS) relies on various technologies to deliver efficient and scalable solutions for different business functions. The specific technologies used can vary based on the type of BaaS and the services offered. Here are some common technologies associated with BaaS:
1. Cloud Computing
2. Blockchain Technology
3. APIs (Application Programming Interfaces)
4. Containerization and Microservices
5. Database Management Systems
6. Security Technologies
7. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
8. DevOps Tools
9. Communication and Collaboration Tools
10. IoT Technologies
11. Analytics and Business Intelligence Tools
Job Role of BaaS (Business-as-a-Service)
Here are some key job roles associated with BaaS:
1. BaaS Consultant/Advisor
2. Cloud Solutions Architect
3. Blockchain Developer
4. Cloud Engineer
5. Data Analyst/Scientist
6. Security Specialist
7. DevOps Engineer
8. Customer Support Specialist
9. Integration Specialist
10. Project Manager
11. AI/ML Engineer
12. IoT Solutions Architect
13. Legal and Regulatory Analyst
14. Sales and Business Development Manager
Salary Expected
The salary for BAAS in AWS in India ranges between 13 lakhs to 35 lakh Per Annum.
Course Highlights
1- Suited for students, fresher’s, professionals, and corporate employees
2- Live online classes
3- 4-month program
4- Certificate of completion
5- Decision Oriented Program of Analysis
6- Live Classes by highly experienced faculties
7- Hands-on experience with real-life case studies

Conclusion
In conclusion, Business as a Service (BaaS) revolutionizes the way businesses operate by leveraging cloud-based solutions. Whether through Blockchain as a Service or broader business functionalities, BaaS enhances scalability, reduces costs, and allows companies to focus on their core strengths. Embracing BaaS empowers businesses with flexibility and efficiency, making it a key player in modern business strategies.

