
Azure Cloud Crash:
Azure Cloud Crash refers to Microsoft’s cloud computing platform, Microsoft Azure, which provides a wide range of services such as virtual computing, storage, networking, and analytics over the internet. It enables businesses to build, deploy, and manage applications and services through a global network of data centers. Azure supports various programming languages, frameworks, and operating systems, offering scalability and flexibility for diverse IT needs.

Fundamentals of Azure Cloud Crash:
Compute Services: Virtual machines (VMs) and serverless computing (Azure Functions).
Storage Solutions: Blob Storage, Table Storage, Azure Files.
Networking: Virtual networks, load balancing, Azure Virtual Network for on-premises connection.
Databases: Azure SQL Database, Cosmos DB (NoSQL), Azure Redis Cache.

Identity and Access Management: Azure Active Directory for user identities and access control.
Security Tools: Azure Security Center, Azure Active Directory Identity Protection.
Monitoring and Management: Azure Monitor, Azure DevOps for continuous integration/deployment.
Development Support: Multi-language and framework support for diverse applications.
AI and ML Services: Azure Machine Learning, Cognitive Services.
Serverless Computing: Azure Functions for building and deploying applications without managing infrastructure.
Types of Azure Cloud Crash
1.Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Azure Virtual Machines (VMs) allow you to deploy and manage VMs in the cloud, providing scalable compute resources.
2.Platform as a Service (PaaS): Azure App Service enables you to build, deploy, and scale web apps, APIs, and mobile backends without managing infrastructure.
3.Software as a Service (SaaS): Azure offers various SaaS applications like Office 365, Dynamics 365, and Microsoft Teams, providing ready-to-use software solutions.
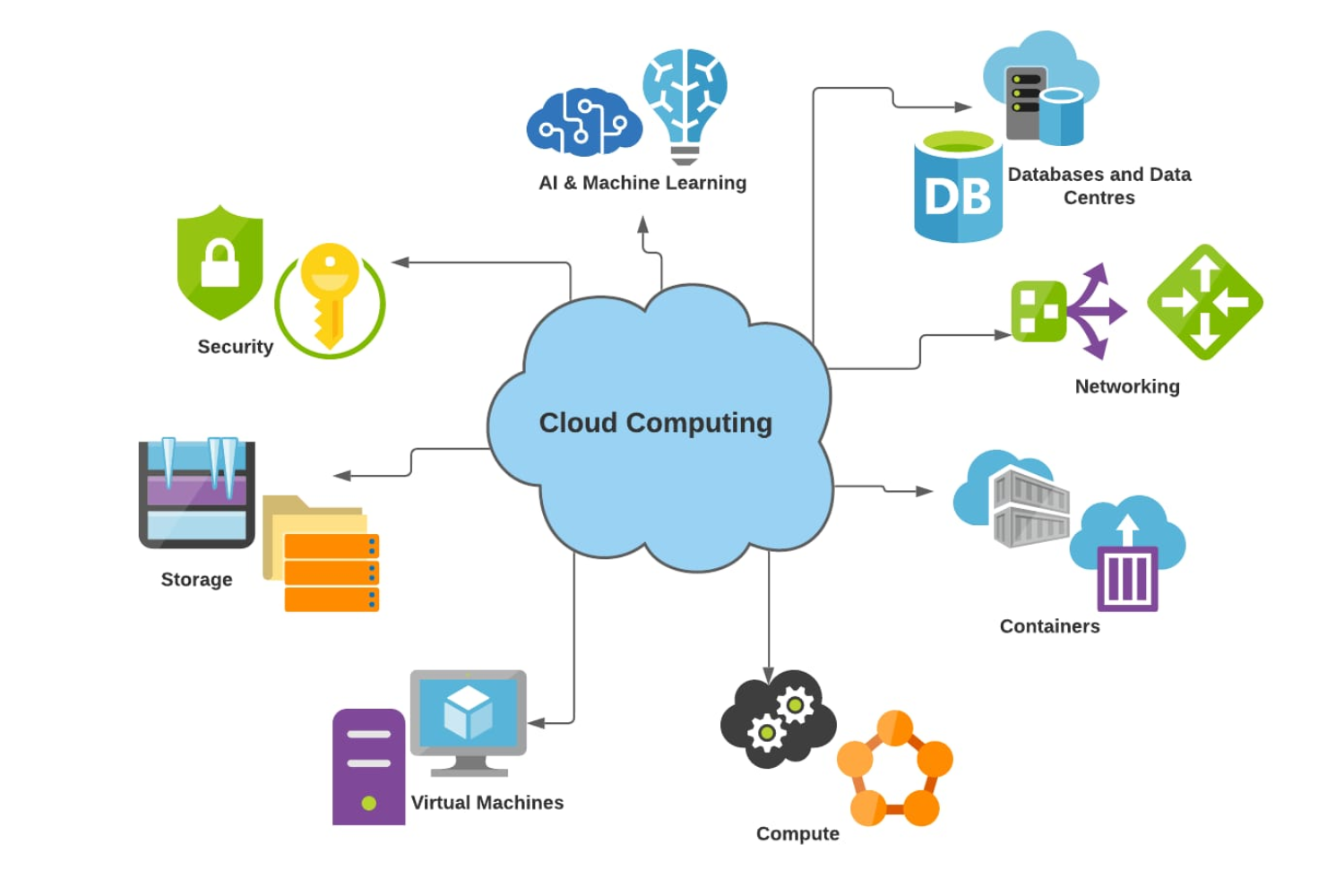
4. Functions as a Service (FaaS): Azure Functions allow you to run event-driven code without provisioning or managing servers, paying only for the resources you consume.
5. Containers as a Service (CaaS): Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) lets you deploy, manage, and scale containerized applications using Kubernetes orchestration.
6. Database as a Service (DBaaS): Azure SQL Database provides fully managed relational databases, removing the need for you to manage infrastructure.
7. Storage as a Service: Azure Blob Storage, Azure Files, and Azure Data Lake Storage offer scalable, secure, and highly available storage solutions.
Benefits of Azure Cloud Crash:
Scalability: Easily scale resources up or down based on demand.
Flexibility: Supports diverse operating systems, programming languages, and frameworks
Cost-Efficiency: Pay-as-you-go model, minimizing upfront costs and optimizing resource usage.
Security: Robust security features and compliance certifications.
Global Presence: Azure has data centers worldwide for low-latency access.
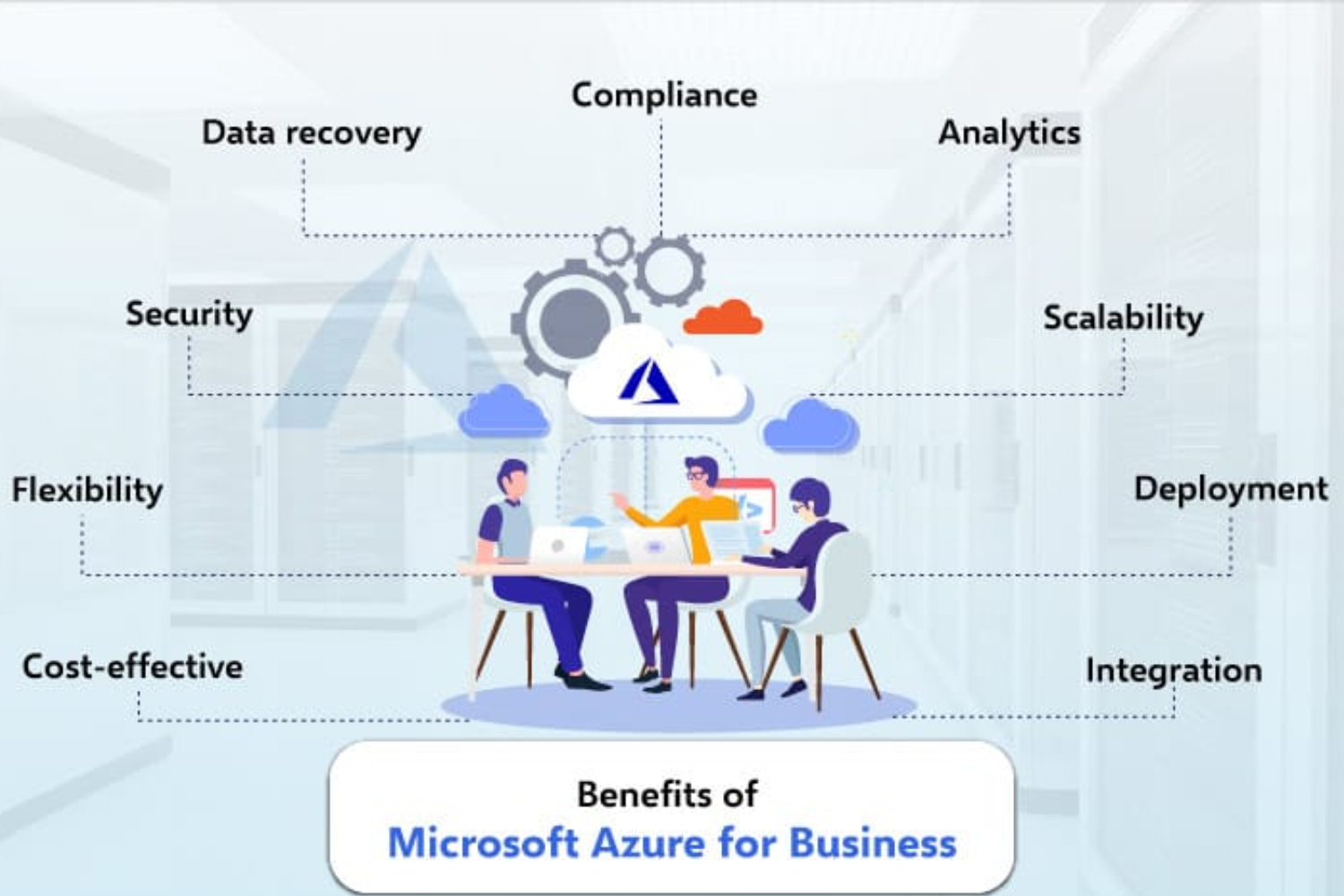
Integration: Seamless integration with other Microsoft products and third-party tools.
Hybrid Capabilities: Connect on-premises infrastructure with cloud services.
Automation: Azure Automation for streamlined management and deployment.
Disaster Recovery: Reliable backup and recovery options for data protection.
Innovation: Regular updates and introduction of cutting-edge services.
Developer-Friendly: Supports various development tools and frameworks
Job Roles in Azure Cloud Computing
1.Cloud Solutions Architect
2.Azure Administrator
3.DevOps Engineer
4.Cloud Developer
5.Data Engineer
6.Security Engineer
7.AI Engineer
8.Network Engineer
9.IoT Developer
10.BI Developer
11.Azure Consultant
Expected Salary:
The average Microsoft Azure Cloud salary ranges from approximately 13 Lakh to 35 Lakh Per Annum
Technologies of Azure Cloud Crash
Azure Virtual Machines: Scalable compute resources for running applications.
Blob Storage: Object storage for unstructured data like images or documents.
Azure SQL Database: Fully managed relational database service.
Cognitive Services: APIs for implementing AI capabilities like vision, speech, and language
Azure App Services: Platform for building, deploying, and scaling web apps.
Azure Functions: Serverless compute service for event-triggered code.
Azure Active Directory: Identity and access management services.
Azure DevOps: Tools for continuous integration, delivery, and collaboration.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS): Managed Kubernetes for containerized applications.
Azure Logic Apps: Visual workflows for automating business processes.
Course Highlights:
1 Suited for students, freshers, professionals, and corporate employees
2 Live online classes
3 15 days program
4 Certificate of completion
5 Decision Oriented Program of Analysis
6 Live Classes by highly experienced faculties
7 Hands-on experience with real-life case studies

Conclusion:
Azure Cloud provides a robust and scalable platform for businesses, offering a wide range of services from computing to analytics. Its global presence, security measures and integration capabilities make it a compelling choice for organizations seeking a flexible and reliable cloud solution. However, careful consideration of specific business needs and cost management is crucial for maximizing the benefits of Azure Cloud.

