
Business Analyst
A Business Analyst is a professional who works to identify and analyze business needs, processes, and problems within an organization. They bridge the gap between business stakeholders and technical teams to help improve efficiency, productivity, and profitability. Business analysts gather and document requirements, create solutions, and facilitate communication to ensure that projects and initiatives align with the organization’s goals and objectives. They play a critical role in making data-driven decisions and driving positive changes in the business.

Fundamental Aspects of Business Analyst:
The following are some essential components of working as a business analyst:
Understanding Business Objectives: Business analysts must have a clear understanding of the organization’s goals and objectives. They need to align their work with these objectives to ensure that the solutions they propose contribute to the overall success of the business.
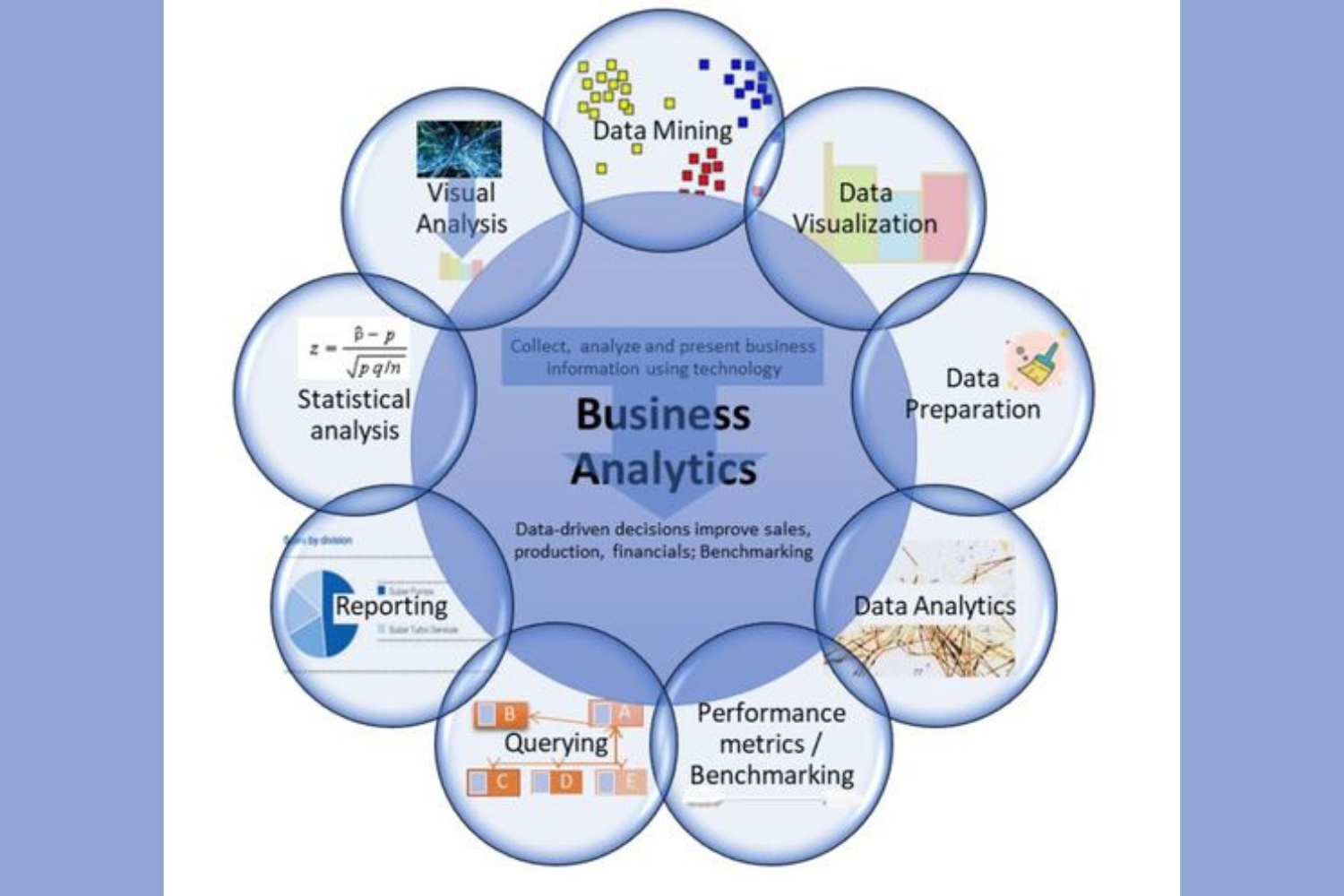
Data Analysis: Business analysts use data to make informed decisions and recommendations. They analyze data to identify trends, patterns, and insights that can guide the business in the right direction.
Requirements Elicitation and Analysis: One of the primary responsibilities of a business analyst is to gather and analyze requirements. This involves identifying and documenting the needs of stakeholders, which serve as the foundation for projects and solutions.
Communication Skills: Effective communication is a core skill for a business analyst. They need to be able to interact with a diverse group of stakeholders, translate technical jargon into understandable terms, and present their findings and recommendations clearly.
Stakeholder Management: Managing relationships with stakeholders, including gathering their input and managing their expectations, is crucial for project success.
Business Process Modeling: Modeling current and future business processes is crucial for understanding how a business operates and how it can be improved. Business analysts use techniques like flowcharts, use cases, and diagrams to represent these processes.
Problem Solving: Business analysts are problem solvers. They identify issues within the organization, analyze their root causes, and propose effective solutions to address these problems.
Documentation and Reporting: Keeping detailed and organized documentation is essential. Business analysts create reports, requirements documents, and other artifacts that serve as references throughout the project or initiative.
Project Management: Business analysts often play a role in project management. They help define project scope, track progress, and ensure that projects stay on track to meet their goals.
Change Management: Managing the process of change within an organization is a vital aspect. Business analysts help ensure that changes are smoothly integrated and that employees and stakeholders are prepared for the changes.
Quality Assurance: Ensuring that the final product or solution meets quality standards and fulfills the specified requirements is part of a business analyst’s responsibility.
Benefits of Business Analyst:
Improved Decision-Making: Business analysts collect and analyze data to provide valuable insights that help organizations make informed decisions. They assess the impact of various options and recommend the most suitable course of action.
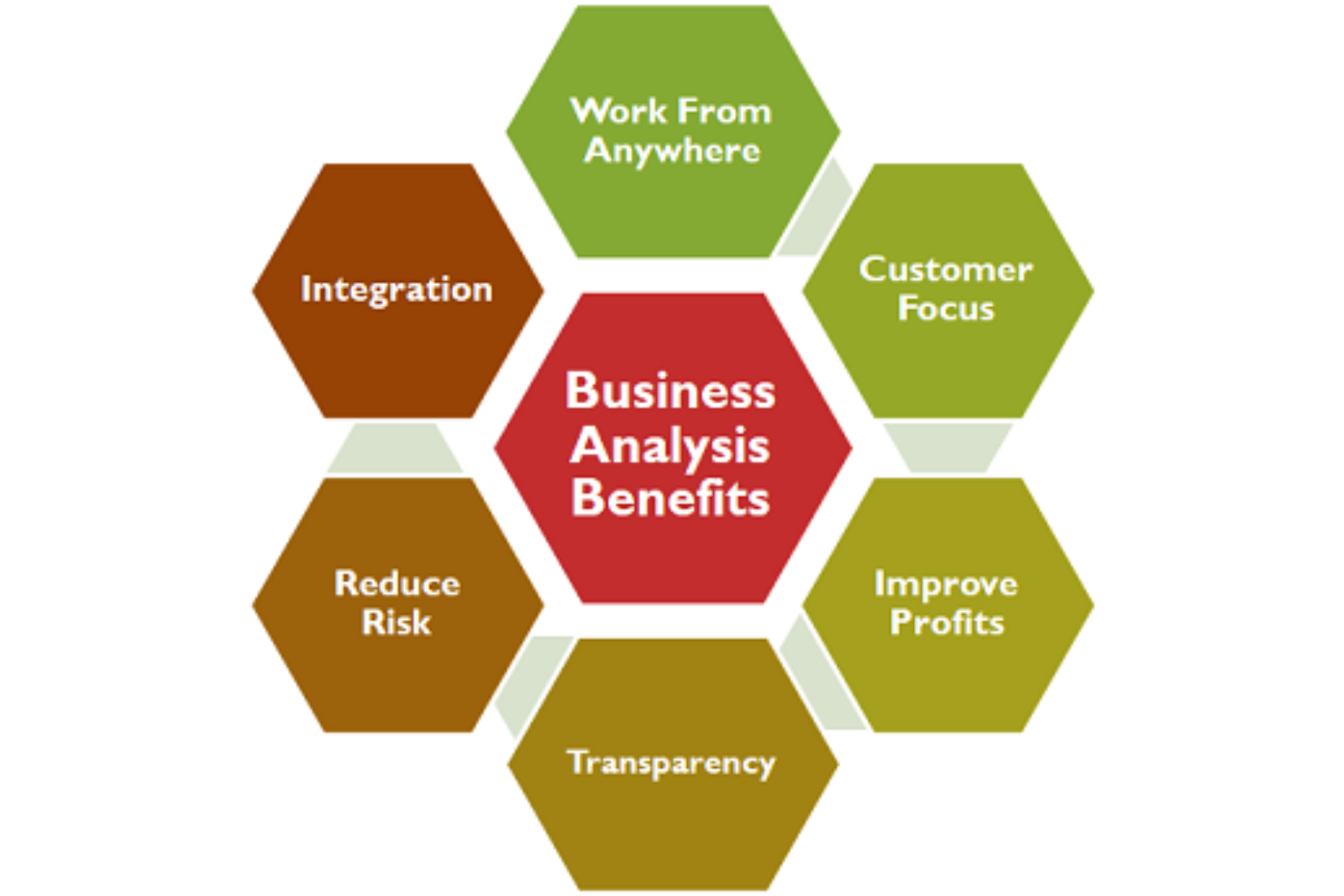
Efficiency and Process Improvement: Business analysts identify inefficiencies in business processes and propose improvements. This can lead to cost savings, increased productivity, and streamlined operations.
Cost Reduction: By optimizing processes and identifying cost-effective solutions, business analysts can contribute to cost reduction and improved profitability.
Requirement Elicitation: They work closely with stakeholders to gather and document business requirements. This ensures that projects and initiatives align with the organization’s goals and meet the needs of its customers.
Customer Satisfaction: Ensuring that projects and systems meet the needs of end-users is a primary responsibility of business analysts. This can lead to higher customer satisfaction and retention.
Communication and Stakeholder Management: They act as a bridge between various stakeholders, including business leaders, IT teams, and end-users. Effective communication and stakeholder management are critical for project success.
Innovation: Business analysts are often involved in identifying opportunities for innovation and helping organizations stay competitive in the rapidly evolving business landscape.
Risk Management: Business analysts identify potential risks associated with projects or business initiatives and develop strategies to mitigate them. This can help prevent costly issues in the future.
Types of Business Analysts:
Business Process Analyst: Focuses on optimizing and improving business processes for increased efficiency.
Systems Analyst: Bridges the gap between business needs and IT solutions, defining system requirements and ensuring technology aligns with business goals.
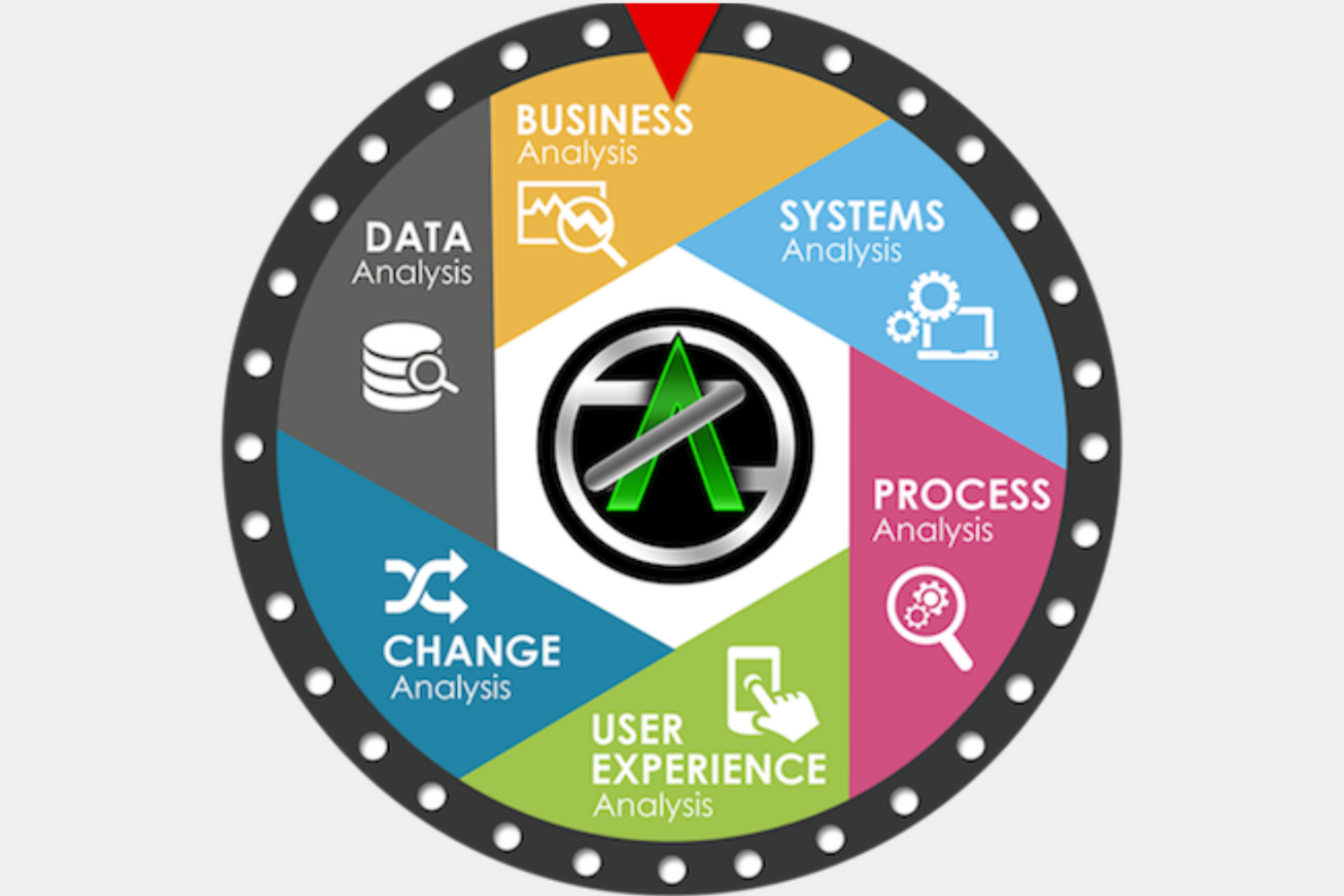
Data Analyst: Collects and analyses data to provide insights for data-driven decision-making.
Financial Analyst: Specializes in financial data and performance, aiding budgeting, investments, and financial planning.
Market Research Analyst: Studies market trends and consumer behaviour to guide product development and marketing strategies.
Business Intelligence (BI) Analyst: Gathers and presents business data to enable data-driven decision-making through reports and visualizations.
Requirements Analyst: Focuses on gathering and documenting project or system requirements to ensure clear, actionable plans.
Quality Assurance Analyst: Tests products, software, or services to ensure they meet quality standards.
Risk Analyst: Assesses and manages risks associated with business activities, such as financial, operational, and compliance risks.
Strategy Analyst: Assists organizations in defining and implementing strategic plans, including competitive analysis and long-term planning.
Career Paths & Opportunities in Business Analyst:
Senior Business Analyst
Business Systems Analyst
Data Analyst
Senior Business Analyst
Business Systems Analyst
Data Analyst
Product Manager
Project Manager
Management Consultant
Business Intelligence Analyst
Process Improvement Analyst
Domain-specific Analyst
Entrepreneur/Start-up Founder
Salary Expected:
Business Analyst salaries can range from 13LPA to 35LPA. SCODEEN Global helps you reach your goals faster by providing you the best advanced Business Analyst course.
Business Analyst Technologies:
Data Analytics: Using data to gain insights.
Excel: Spreadsheet software for analysis.
SQL: Query language for databases.
Tableau: Data visualization tool.
Python: Programming language for data analysis.
Power BI: Business intelligence platform.
Jira: Project management and issue tracking.
Agile: Methodology for project management.
CRM (Customer Relationship Management): Managing customer data and interactions.
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load): Data integration process.
UML (Unified Modeling Language): Diagrams for software design.
SWOT Analysis: Assessing strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Machine Learning: Algorithms for predictive analysis.
Data Warehousing: Centralized data storage for analysis.
Cloud Computing: Hosting and scaling IT resources.
Competitive Analysis: Evaluating competitors in the market.
Data Mining: Discovering patterns in large datasets.
Stakeholder: Individuals or groups with an interest in the project
Skills You will learn from Business Analyst Course:
Capabilities for Analytical Problem Solving
Consultation and interpersonal skills
Proficiency in both written and oral communication
Basic abilities and knowledge of software
Basic knowledge of programming languages
Knowledge of Networks and Databases
Expertise in the field
Understanding of business structures
Understanding of Related Tools, such as: Stakeholder Analysis for Blueprint
Benefit-Cost Analysis
Prerequisites Modelling of engineering processes
Imaginative attitude
Course Highlights:
1- Suited for students, freshers, professionals, and corporate employees
2- Live online classes
3- 4-month program
4- Certificate of completion
5- Decision Oriented Program of Analysis
6- Live Classes by highly experienced faculties
7- Hands-on experience with real-life case studies

Conclusion:
In conclusion, a business analyst’s contributions are instrumental in helping businesses make informed decisions, optimize processes, enhance efficiency, and ultimately achieve their goals. They act as a bridge between technical and business teams, ensuring that technology investments align with the organization’s strategic vision. Effective business analysis can lead to cost savings, revenue growth, and improved customer satisfaction, making business analysts essential to a company’s success. All these features make Business Analyst a smart career choice.

