
Process Engineering
Process engineering is a multidisciplinary field that focuses on designing, optimizing, and managing industrial processes to transform raw materials into valuable products efficiently and safely. It encompasses a range of industries, including chemical, manufacturing, and energy production. Process engineers use principles of chemistry, physics, and engineering to develop and implement processes that meet specific product quality, cost, and sustainability objectives. They analyze, model, and improve processes, taking into account factors like equipment selection, material flow, heat and mass transfer, and safety measures. Overall, process engineering aims to enhance productivity, reduce waste, and ensure the reliable and economical production of goods.
FUNDAMENTALS OF PROCESS ENGINEERING
TYPES OF PROCESS ENGINEERING
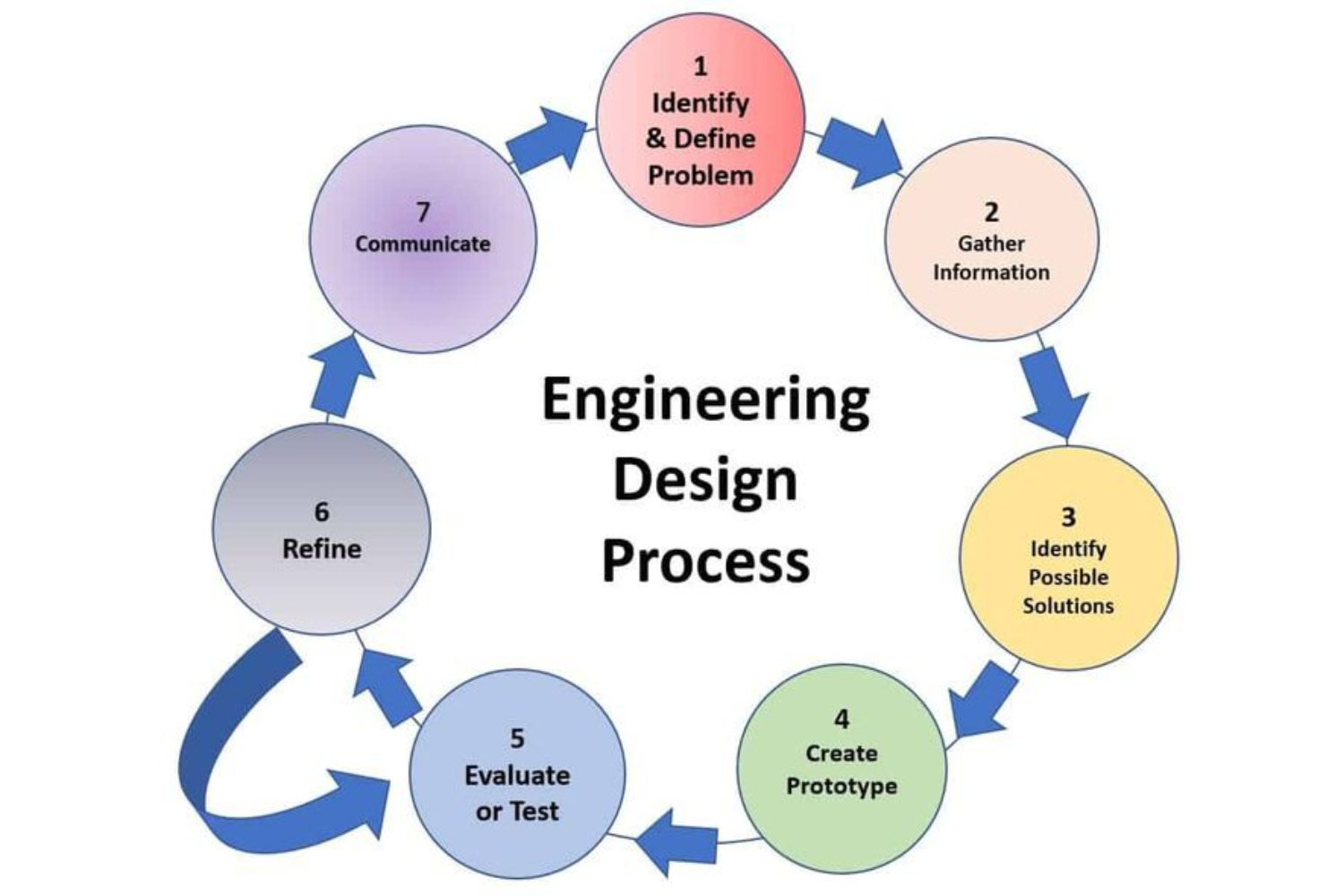
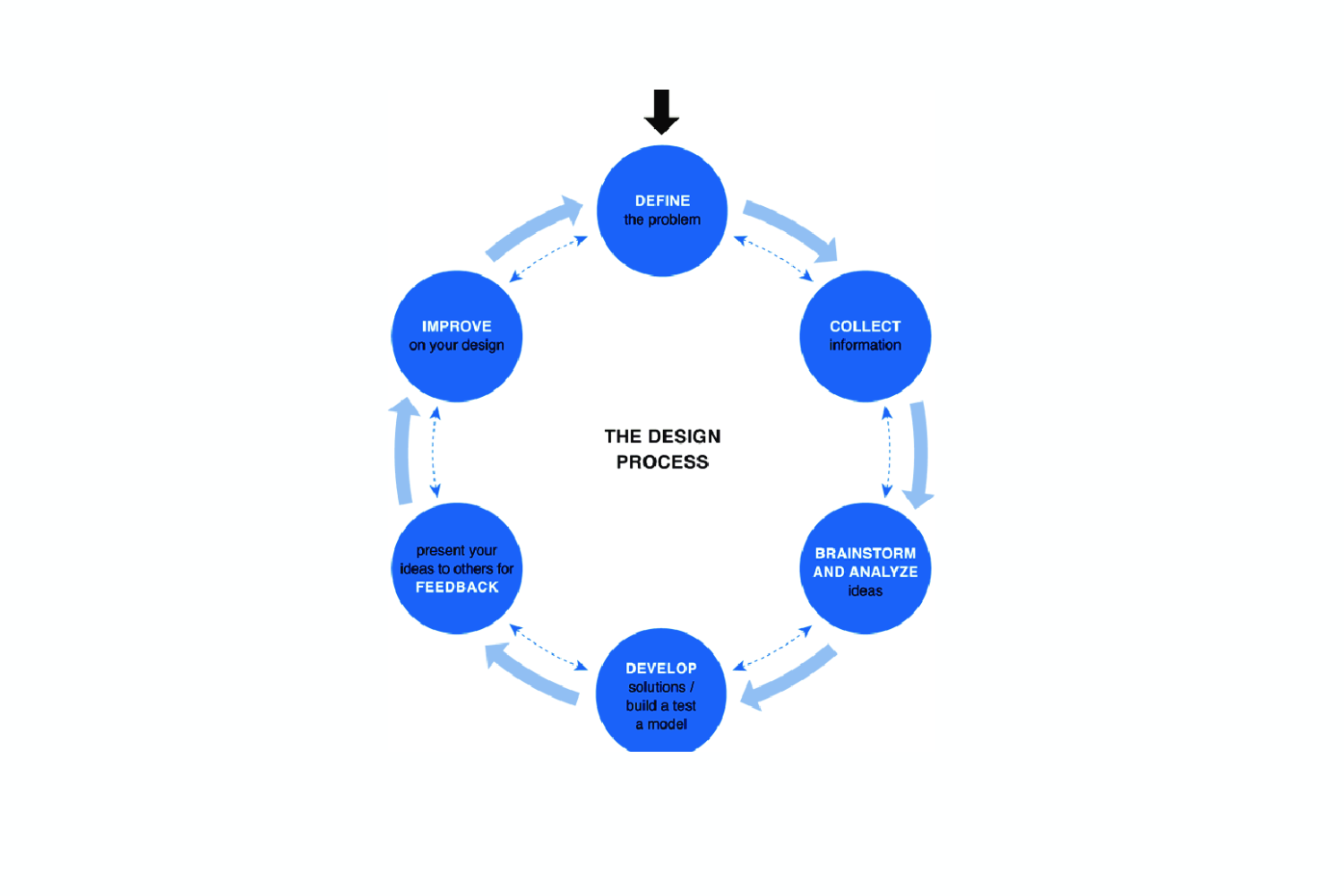
SCOPE OF PROCESS ENGINEERING
The scope of Process Engineering is extensive and continues to evolve in response to the dynamic demands of various industries. In essence, it involves the design, optimization, and management of production processes to ensure efficiency, quality, and safety. Within the chemical and petrochemical industries, Process Engineers are essential for creating and maintaining safe, efficient, and environmentally compliant operations. In manufacturing, they contribute to cost-effective and high-quality production methods, encompassing diverse processes such as metalworking, casting, and additive manufacturing. In biotechnology and pharmaceuticals, Process Engineering is crucial for the efficient and consistent production of pharmaceuticals and biopharmaceuticals. Additionally, it plays a pivotal role in environmental engineering by focusing on waste management, pollution control, and sustainability in areas like wastewater treatment and renewable energy. In the aerospace, electronics, and materials sectors, Process Engineers drive innovation and precision in manufacturing. With an ever-expanding scope, Process Engineering is indispensable in addressing modern challenges and ensuring sustainable, efficient, and safe production across a wide range of industries.
TECHNOLOGIES OF PROCESS ENGINEERING
Process Engineering relies on a range of technologies to design, optimize, and manage production processes efficiently. These technologies play a vital role in improving product quality, reducing waste, and ensuring safety in various industries. Some key technologies in Process Engineering include:
Process Simulation Software: Utilized for modeling and analyzing processes before implementation, ensuring optimal design and performance.
Control Systems: Encompassing Distributed Control Systems (DCS) and SCADA, these technologies enable real-time monitoring and automated control of industrial processes.
Process Automation: PLCs, Ion, and robotics enhance efficiency by automating tasks and process control, reducing human error.
Chemical Engineering Software: Tools like MATLAB and COMSOL aid in complex calculations, optimizing chemical reactions and designing chemical processes.
Computer-Aided Design (CAD): CAD software facilitates equipment and facility design, aiding in process visualization and planning.
Data Analytics and Machine Learning: Employed for data-driven decision-making, predictive maintenance, and process optimization.
Sensors and Instrumentation: Various sensors provide crucial real-time data for monitoring and control.
Process Safety Systems: Technologies like SIS and HAZOP ensure process safety, identifying and mitigating potential risks.
Materials and Corrosion Technologies: Essential for selecting materials and preventing corrosion, ensuring equipment durability and product quality.
Renewable and Sustainable Technologies: Integration of sustainable practices and renewable energy sources to reduce environmental impact.
Nanotechnology: Applied in materials and pharmaceuticals for precision engineering and property manipulation at the nanoscale.
3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing: These technologies revolutionize manufacturing and materials engineering by enabling precise and complex component production.
Energy Management Systems: Technologies for monitoring and optimizing energy consumption in industrial processes, contributing to cost savings and sustainability.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): Utilized for training and maintenance, allowing engineers to visualize and interact with complex processes and equipment.
Bioprocess Technologies: Encompassing bioreactors, fermentation, and genetic engineering, these technologies support the production of biopharmaceuticals and biofuels.
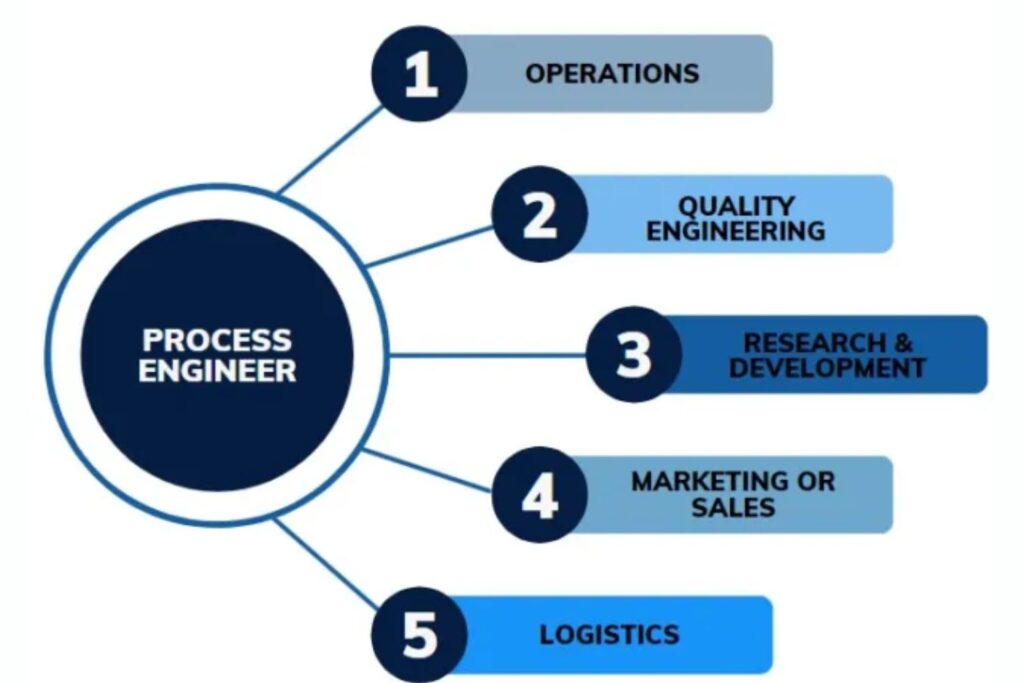
JOB ROLE OF PROCESS ENGINEERING

COURSE HIGHLIGHTS
1. Suited for students, fresher’s, professionals, and corporate employees
2. Live online classes
3. 4-Month program.
4. Certificate of completion
5. Decision Oriented Program of Analysis
6. Live Classes by highly experienced faculties
7. Hands-on experience with real-life case studies
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, Process Engineering is a field of engineering that focuses on designing, optimizing, and managing industrial processes to efficiently produce desired products. It involves a systematic approach to analyze, model, and control various operations, ensuring safety, cost-effectiveness, and environmental sustainability. The Process Engineering plays a pivotal role in industries like chemical, petrochemical, food, and pharmaceutical, enabling them to streamline production, improve product quality, and minimize waste. It’s essential for innovation and the development of novel technologies while adhering to stringent regulatory and safety standards, ultimately contributing to industrial success and economic growth.

